The basics for restful sleep
Sleep is crucial for physical and mental health. However, it can be challenging to get enough restful sleep every night. The effects of poor sleep can impact all areas of life. The sleep habits you maintain daily - also known as sleep hygiene - can have a positive influence on how well you sleep.
1. Invest in a high-quality mattress and bedding
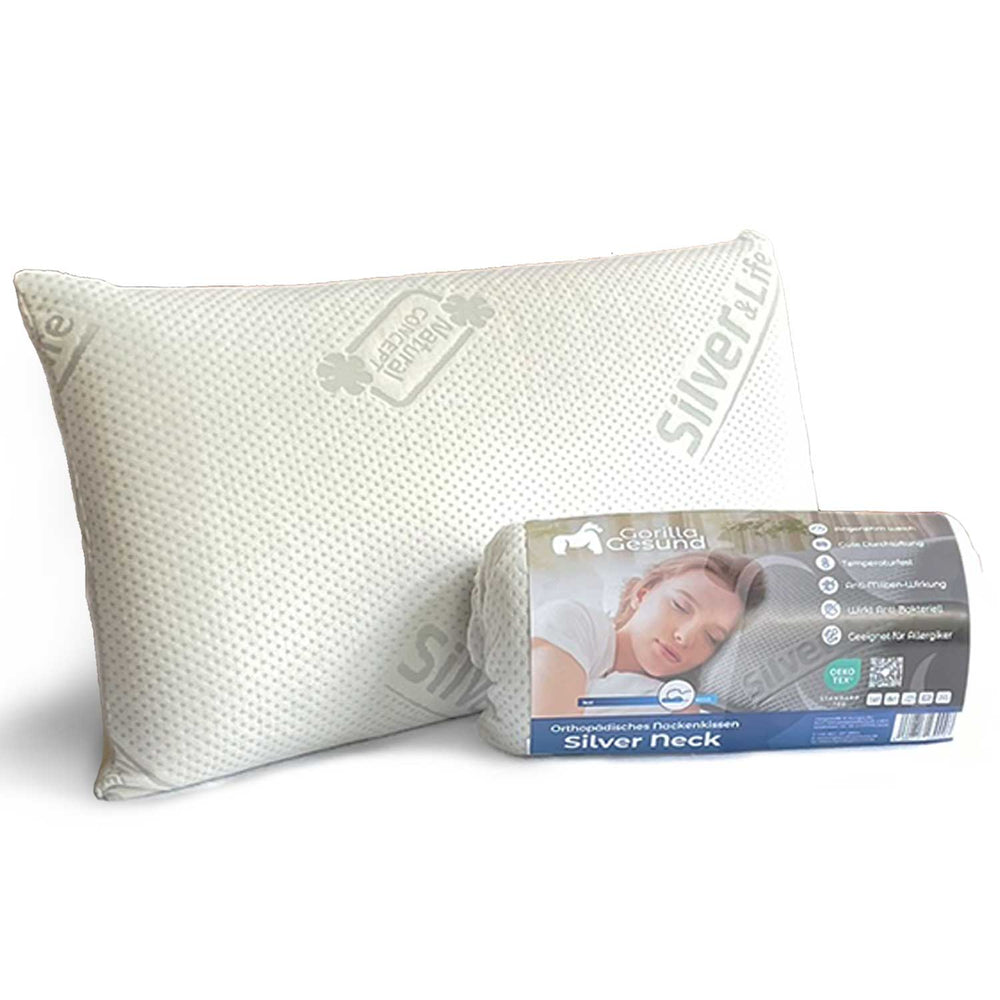
Choosing the right mattress that suits your needs and preferences is crucial to ensure you can relax sufficiently. A supportive mattress and an ergonomic pillow provide correct spinal support to avoid pain. Your bed linens and blankets also play an important role in making your bed inviting. Pay attention to bedding that feels comfortable and maintains a pleasant temperature throughout the night.
2. Block out light
Excessive light exposure can affect your sleep and circadian rhythm. Blackout curtains on your windows or a sleep mask over your eyes can block light and minimize disruptive influences on your rest. Avoiding bright light can help you prepare for bedtime and promote the production of melatonin, a hormone that supports sleep.
3. Minimize noise
Low noise is an important part of a sleep-friendly bedroom. If you cannot completely eliminate noise sources, consider using a fan or a white noise machine to mask disturbing sounds. Earplugs or headphones are another option to minimize disruptive noises while sleeping.
4. The ideal room temperature
The room temperature should be neither too hot nor too cold to distract from your sleep. The ideal temperature can vary individually, but studies support the idea that a cool room of about 18 to 20 degrees Celsius is conducive to sleep.
5. Plan enough sleep time
To ensure you get enough sleep every night, it is important to schedule this time into your daily routine. Consider your fixed wake-up time and set a target bedtime that allows for at least seven hours of sleep. If possible, give yourself extra time before going to bed to prepare for sleep.
6. Set regular wake-up times
Your body can only adjust with difficulty to a healthy sleep cycle if you constantly wake up at different times. Choose a fixed wake-up time and stick to it even on weekends or other days when you would normally sleep longer.
7. Short naps
To sleep better at night, it is important to be cautious with naps. If you sleep too long or too late in the day, it can disrupt your sleep cycle and make it harder to fall asleep. The best time for a nap is shortly after lunch in the early afternoon, and the ideal duration is about 20 minutes.
8. Relax before bedtime
It is much easier to fall asleep when you feel relaxed. Reading, gentle stretching, soothing music, and relaxation exercises are examples of ways to get into the right mindset for sleep. Focus on relaxing rather than forcing yourself to fall asleep. Controlled breathing, mindfulness meditation, progressive muscle relaxation, and guided imagery are examples of relaxation techniques that can help you fall asleep.
9. Avoid electronic devices before bedtime
Tablets, smartphones, and laptops can stimulate your brain and make it difficult to relax. The light from these electronic devices can also suppress the natural production of melatonin. Try to disconnect from electronic devices an hour or more before bedtime.
10. Daylight exposure
The body's internal clock is regulated by light exposure. Sunlight has a strong effect on our body. Try to get daylight by going outdoors or opening windows and blinds. A dose of daylight early in the morning can help normalize your circadian rhythm.
11. Daily exercise
Daily physical activity has many health benefits and can contribute to restful sleep. The changes it causes in energy expenditure and body temperature promote healthy sleep. However, avoid intense exercise shortly before bedtime, as this can impair your body's ability to wind down before sleep.
12. Limit caffeine after 2 PM
Caffeinated drinks like coffee, tea, and sodas are popular worldwide. Some people try to stay awake during the day with the help of caffeine, but this approach is not sustainable and can cause long-term sleep deprivation. Be sure to monitor your caffeine intake and avoid it later in the day to not interfere with falling asleep.
13. Alcohol consumption before bedtime
Alcohol can cause drowsiness, so some people like to take a sleeping aid before going to bed. Unfortunately, alcohol affects the brain in ways that can impair sleep quality. It is best to avoid alcohol consumption before bedtime.
14. Have dinner a few hours before bedtime
It can be harder to fall asleep if your body is still digesting a large meal. Avoid late dinners and reduce particularly fatty or spicy foods to minimize sleep disturbances caused by food intake. If you need an evening snack, choose something light.
15. Limit nicotine consumption and smoke exposure
Exposure to smoke, including secondhand smoke, has been linked to a variety of sleep problems, including difficulty falling asleep and fragmented sleep. Nicotine is a stimulant, and especially consuming it in the evening can impair sleep.
16. Reserve your bed for sleep and sex
If you have a comfortable bed, you might be tempted to spend your leisure time there, but this can actually lead to sleep problems. You want to create a strong mental association between your bed and sleep, so activities in bed should be limited to sleep and sex.
17. Leave the bed after 20 minutes
You want to avoid associating your bed with frustration due to insomnia. If you have spent about 20 minutes in bed without being able to fall asleep, it is best to get up and do something relaxing in dim light. Avoid looking at the clock or using electronic devices, and return to bed as soon as you feel tired.
18. Keep a sleep journal
A daily sleep journal can help you track your sleep quality and identify factors that might affect your sleep. If you are trying a new sleep schedule or other changes in sleep hygiene, your sleep log can document how well it works.
19. Consider supplements
In addition to improving overall sleep hygiene, you may want to talk to your doctor about using supplements. Melatonin supplements are commonly used to shorten the time it takes to fall asleep. Other natural sleep aids include valerian, chamomile, and glycine. Since supplements are not strictly regulated by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, you should take steps to ensure you purchase reputable sleep aids.
20. Consult a doctor
Your doctor is in the best position to provide detailed and personalized advice if you have serious sleep difficulties. Talk to your doctor if you find that your sleep problems worsen, persist long-term, affect your health and safety, or occur with other unexplained health issues. Your doctor can offer additional guidance and treat possible underlying conditions.